Allergy-prone skin is difficult to take care of because it doesn’t tolerate a majority of cosmetics well, also hard water and even some nutrients. Although it has a genetic basis, it can become active at any age – under the influence of various factors. It also happens that the skin that has never caused any problems becomes allergic. How to identify allergic skin and distinguish it from sensitive and couperose skin? How to take care of for allergic skin and what can be harmful to it? I will try to answer these and other questions in a moment.
How to identify allergy-prone skin and tell it form a sensitive and couperose skin?
Allergy-prone vs sensitive skin
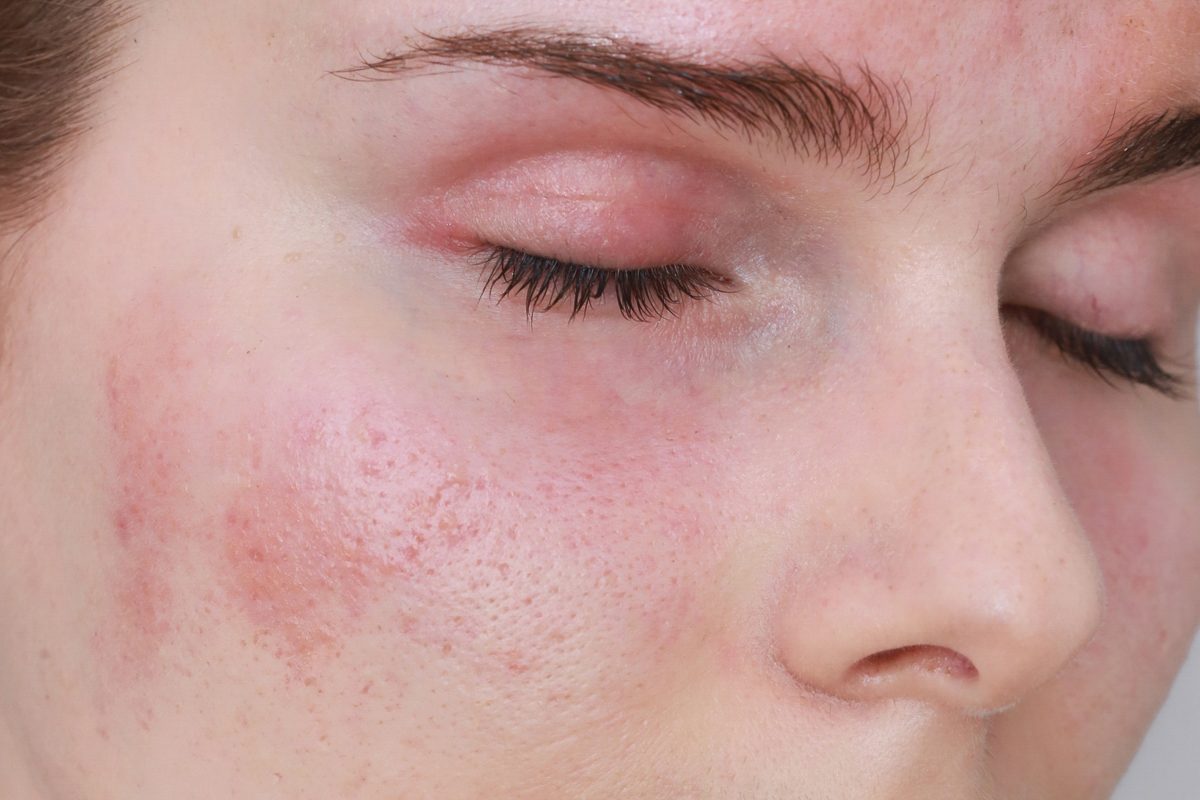
Allergic skin can be associated with sensitive skin because it reacts similarly to irritants: burning sensation, erythema, itching, and sometimes a rash. They are also connected by the structure: both are shallowly vascularized which is indicated by small blood vessels that show through the skin. In addition, both types differ from healthy skin due to a damaged lipid barrier of the epidermis, and also its stratum corneum. In turn, the mechanism of change creation is what helps tell them apart.
Unpleasant sensations accompanying the allergic skin, such as pruritus, burning or erythema, are caused by allergens that penetrate the damaged epidermal barrier and consequently cause an inflammatory reaction. On the other hand, in the case of sensitive skin, skin changes appear almost immediately after contact with an irritant.
The first contact with the allergen triggers an allergic reaction in the body, which only becomes known after repeated contact with this substance. Therefore, if you use a new cosmetic for the first time you will feel that your skin does not tolerate it, probably it is only sensitive. However, if an allergic reaction occurs only after another application of the preparation, it’s most likely you have an allergic skin.
Another determinant of allergic skin are the so-called distant reactions. Although you have applied the cosmetic to the face, urticaria or swelling appears on the hands, stomach or cleavage. In addition, changes in the allergic skin rarely disappear on their own – they go away only after taking antihistamine medicine or calcium.
It is not easy to distinguish between allergy and sensitive skin independently, so it is better not to make a diagnosis on your own. The dermatologist will take into account criteria such as the time of change development, location, and size, and then tell you the cause and come up with a course of treatment.
Allergy-prone skin vs couperose skin
In the case of couperose skin, skin lesions appear as the effects of external factors such as frost, sun or wind, but in a sudden change in temperature (return from cold outdoors into a heated apartment) – then the skin becomes red. In this type of skin, the capillaries are located much shallower than in other cases. Couperose skin is not a disease; erythema is the result of genetic and hormonal factors (the probability of its occurrence increases when estrogen production increases – hence, it affects women more often than men).
Is allergic skin also sensitive?
Allergic skin is always sensitive, but sensitive skin does not have to be allergic. Sensitivity is an acquired trait that occurs, for example, due to prolonged improper care, while the tendency to allergy is genetically determined.
How to take care of allergy-prone skin?
Allergic skin must be taken care of similarly to sensitive skin. The cosmetics must be well-chosen, and it’s advisable to avoid hard and chlorinated water.
All the products you use must be hypoallergenic, fragrance-free and dedicated to atopic dermatitis. Furthermore, they must have a pH of 5.5 and protect the skin against harmful external factors, rebuild the lipid barrier, provide anti-inflammatory qualities, bring relief to irritation and regenerate the stratum corneum. All cosmetics should come from the same series – this will reduce the risk of sensitization.
Moreover, in order to cleanse the skin, you can go ahead and use lotions designed for atopic dermatitis and dermatological soap bars. Remember to avoid cosmetics with exfoliating properties! Allergy-prone skin can be exfoliated once a month only with the use of enzyme peels.
Additionally, the cosmetics used on a daily basis must comprise mineral sunscreens (such as titanium dioxide, zinc oxide or mica), because they are less likely to cause allergic reactions. Twice a week, I recommend you apply a soothing mask.
What is harmful to allergy-prone skin?
Allergy-prone skin care is not an easy task to fulfill because allergens contained in cosmetics are the ones to cause pruritus, burning or exacerbation of existing lesions. The most common allergens are lanolin, propylene glycol, pigments found in colored cosmetics, preservatives, and fragrances. In addition, stress, air pollution, staying in air-conditioned rooms and the simultaneous use of too many cosmetics are a serious threat to the allergic skin.
Furthermore, one of the symptoms associated with allergic skin may be food allergies; it can be suspected if skin changes have occurred after the consumption of a specific product. In this situation, you must go to an allergist to run tests that will determine the allergen. Excluding it from the menu should improve the skin condition.
And how do you take care of allergic complexion and at what age has it been revealed? Please, Share your experiences!




Leave a Reply